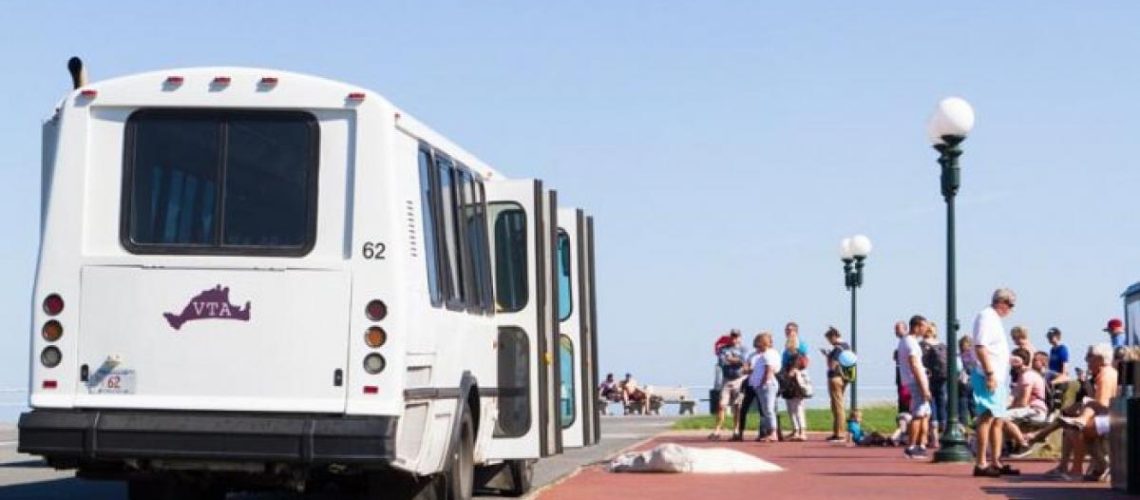
An electric bus charging station on Martha’s Vineyard is using microgrid controllers to turn solar-plus-storage EV charging centers into microgrids that provide power when the grid goes down.
The Martha’s Vineyard Transit Authority (VTA) had a vision of transitioning its fleet of buses to all electric. To assist with that transition, it partnered with the Vermont Energy Investment Corporation (VEIC), a Vermont-based non-profit organization that helps companies and organizations become more energy efficient and less dependent on fossil fuels. As an island, Martha’s Vineyard (MV) gets its fossil fuels from the mainland, so by going electric, with buses charged by solar, the VTA is creating a more sustainable transportation system for the island.
The VTA purchased its first electric buses in 2018 to serve the nearly 1.3 million residents and tourists that use the MV transit system each year. A solar canopy at the charging station became operational in 2021, and the fleet has more than doubled. The next step to ensure reliability was to turn the charging station into a microgrid that could island when the grid goes down, and battery storage was added.
To manage the microgrid, the VTA turned to PXiSE Energy Solutions (pronounced ‘Pice’) for a microgrid controller to automate the integration of multiple distributed energy generation resources, including a 466kW solar array, a battery storage system and 16 bus charging stations. The microgrid controllers enable the charging centers to stay up and running for several hours in the event of a power outage, and they also they provide real-time forecasting that provides additional functions such as real-time asset control and tight ramp-rate control. The microgrid controllers ensure connectivity to virtually any device on the grid, according to PXiSE, and they aggregate power from the solar and battery systems, creating a single virtual power plant that can operate off grid.
PXiSE Energy Solutions recently announced that Rove Charging, a California-based company that designs and builds EV charging centers, will use its microgrid controller with battery storage and onsite solar. Rove’s EV charging centers are designed to host more than 40 direct current fast chargers (DCFC), an onsite market, car wash, 24/7 lounge, dog walk and restroom facilities. For Rove’s centers, the PXiSE software solution will manage the point of interconnection with the utility to a net-zero export, while also managing the facility’s generation capability
“This advanced controller will allow us to better leverage renewable energy from the California grid and Rove’s onsite solar to provide more affordable, sustainable, and reliable charging to Rove customers,” said Nathan McDonnell, chief executive officer of Rove.